A More Holistic View for Graph AI: New Pooling Method Boosts Performance in Drug Discovery and Network Analysis
A new study from the ZHAW Centre for Artificial Intelligence, in collaboration with Università Ca’ Foscari Venezia, introduces DSMVPool, a multi-view graph pooling method published in Pattern Recognition. The approach overcomes key limitations in how AI models summarize complex relational data, leading to significant performance improvements in diverse areas such as chemical informatics, social network analysis, and computer vision.
Ever wondered how AI can understand complex structures like social networks or molecules? A key tool for this is Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). But to truly make sense of an entire graph, they need an effective way to summarise it—a process known as "graph pooling."
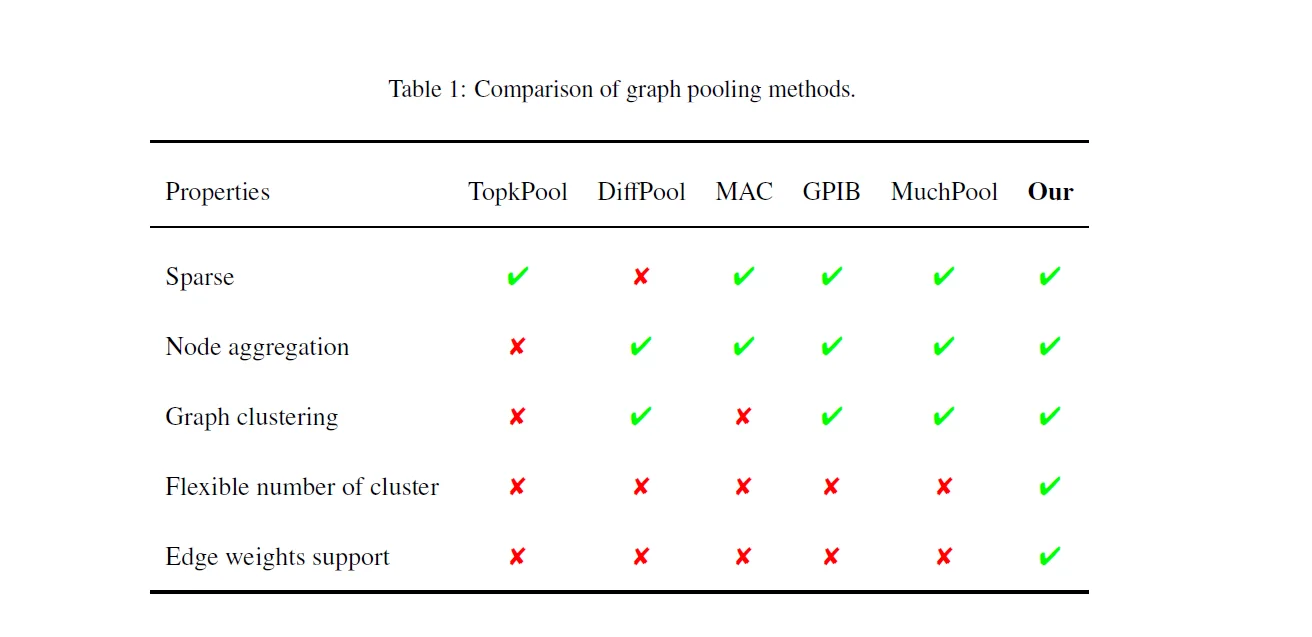
The problem? Most pooling techniques are like trying to describe a city by only looking at its main streets, ignoring the intricate alleyways (local details), the major highways connecting districts (global structure), and the key landmarks that define its character (critical features). They also miss the "strength" of these connections (edge weights).
This is the challenge we tackled head-on in our latest paper, “Multi-view Graph Pooling via Dominant Sets for Graph Classification,” published in the journal Pattern Recognition.
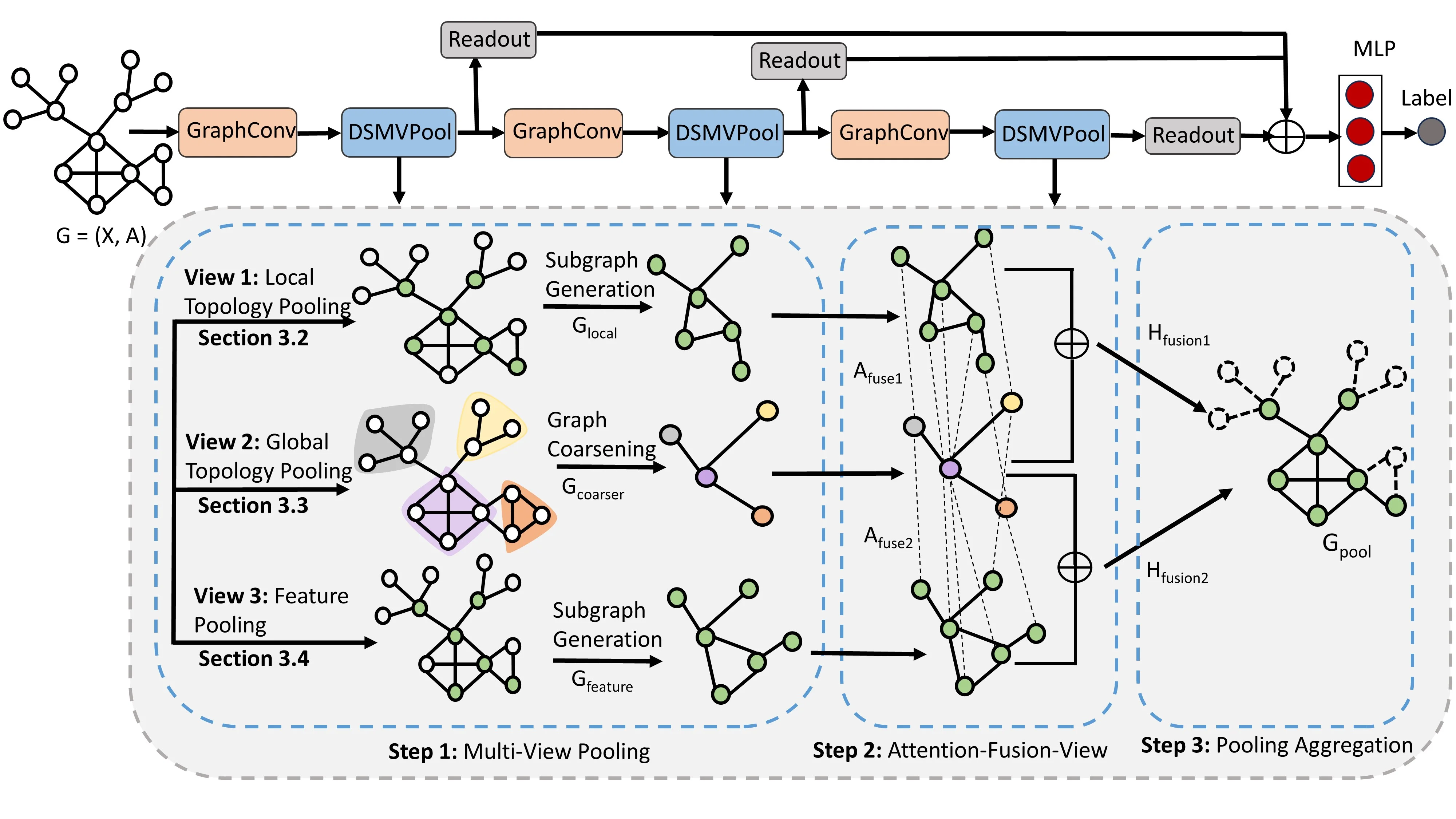
The solution? A novel method named DSMVPool, which acts like a team of expert city planners to get a complete, multi-view understanding of any graph.
Think of it as deploying three specialised virtual experts:
- The Local Guide: Focuses on the dynamics of immediate neighbourhoods and alleyways.
- The Global Architect: Analyses the city's overall layout, identifying major districts and communities using a flexible "Dominant Set" clustering method that doesn't require a pre-defined map.
- The Feature Analyst: Pinpoints the most influential and characteristic landmarks.
Our innovative fusion-view attention layer then acts as the lead project manager, intelligently combining all three reports into one perfect, comprehensive summary. This ensures that the final graph representation captures both the forest and the trees.
The real-world impact of this multi-perspective approach is profound:
- In Drug Discovery: For a molecule, DSMVPool can identify crucial atomic groups and understand the strength of the chemical bonds between them. This leads to more accurate predictions of a molecule's properties, potentially accelerating the design of new pharmaceuticals.
- In Social Network Analysis: The method naturally detects tight-knit communities based on the intensity and frequency of interactions, not just the mere existence of a connection. This is vital for accurately identifying influential communities or coordinated behaviour.
- In Computer Vision and Bioinformatics: The ability to simultaneously grasp fine details and the big picture improves the classification of protein structures and the interpretation of complex scenes in images.
This work marks a crucial step towards building AI systems that can reason about our complex, interconnected world with the nuance and depth that it deserves.