System for integrated, data-driven asset controlling of real estate (SIDAC2)
Description
The aim of the SIDAC2 project is an integrated system for the valuation and management of existing real estate. The SIDAC2 project team was made up of ZHAW researchers from the Institute for Facility Management (IFM), the Institute for Administration and Management (IVM) and the Institute for Applied Information Technology (InIT). QualiCasa AG and a2-c AG were involved in the project as industrial partners. Together, the SIDAC2 software system was further developed and new real estate services realized.
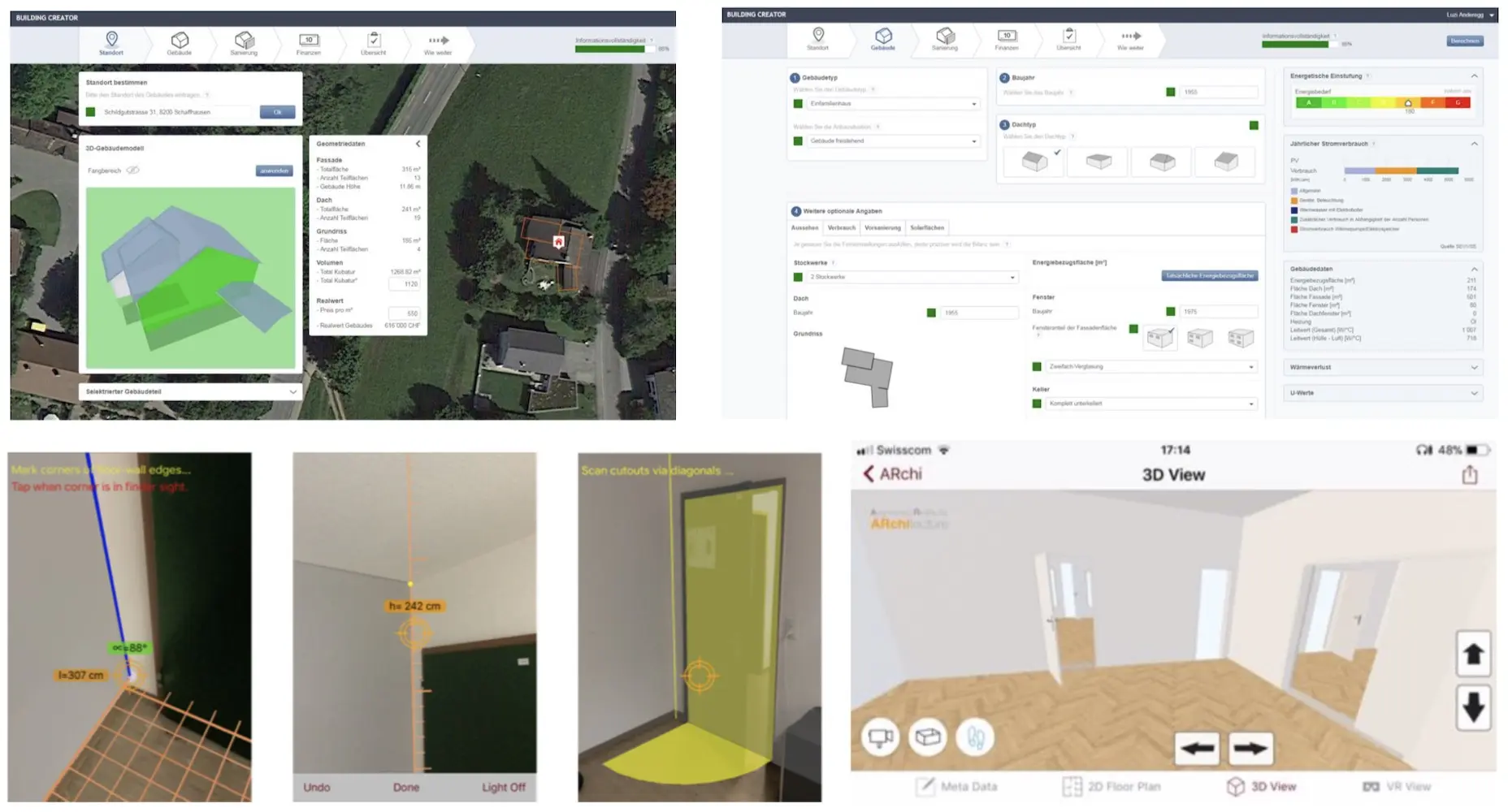
The two extended main functions of SIDAC2 relate to data collection and simulation. There is a great need for the collection of existing real estate, since there are often no or not up-to-date 2D architectural plans and the actual situation has to be tracked over the years. In the SIDAC2 project, the following approaches were followed, developed and field-tested:
- Modeling in CAD tools with manual maintenance of metadata
- Building and room acquisition using a laser scanner and subsequent processing of 3D and meta data
- Automated generation of building envelopes from swisstopo aerial photographs with derivation of metadata according to hedonic and empirical approaches
- Indoor room capturing with mobile devices using Augmented Reality (AR)
The R&D work by SIDAC2 focused on smart solutions in order to obtain application-oriented 3D building models with the least possible effort. For the mobile room capturing, the Google Tango device with depth camera was first used. Towards the end of the project, Apple released with ARKit a new technology that enables new-generation iPhones (without a special camera) to provide similar 3D recognition capabilities, which has been positively demonstrated as a technological feasibility with the ARchi VR app.
Digital space capturing aims to improve downstream processes such as asset & facility management, maintenance and cost controlling in the usage phase of real estate. For this purpose, the geometric 2D and 3D data must be supplemented with additional information (such as metadata about object types, materialization, age, area separations, etc.). This integrated building information (as Building Information Model, BIM) can thus be used for more than just in the classic construction phase. However, real estate managers and financial service providers have different requirements for the scope and precision of data than architects and energy planners.For this enhanced use of BIM, Qualicasa's data-driven pricing model has evolved to holistically consider lifecycle costing (LCC). For the integration of BIM and LCC, the classification of the trades and components is the key to linking the widest variety of data sources.
For this purpose, the eBKP classification system (electronic construction cost plan, eBKP, www.crb.ch) was used in the field test for the coordination between BIM and LCC simulation. In addition to empirical data on component lifetime, regional factors (cantonal legislation, conditions of building insurance) were also included in the calculation scheme. Based on the LCC calculation, detailed simulations of investment and renovation planning for the preservation of real estate can be calculated from the collected building data, age of the trades, price development and financing costs.
The integration of BIM and LCC increases the planning accuracy of investment and renovation projects for housing inventories. This approach is likely to show practical and financial improvements in the construction industry and in real estate management.
Key data
Projectlead
Project partners
QualiCasa AG; a2-c AG
Project status
completed, 03/2016 - 12/2017
Institute/Centre
Institute of Computer Science (InIT); Institute of Facility Management (IFM); Institute of Public Management (IVM)
Funding partner
KTI-Projekt / Projekt Nr. 18490.1 PFES-ES