Completed MSE-Project Theses
All MSE-Students have to complete between two and four project theses during their Master Course at IMS. The following are some example projects.
Robot-assisted Single-Cut-Osteotomy
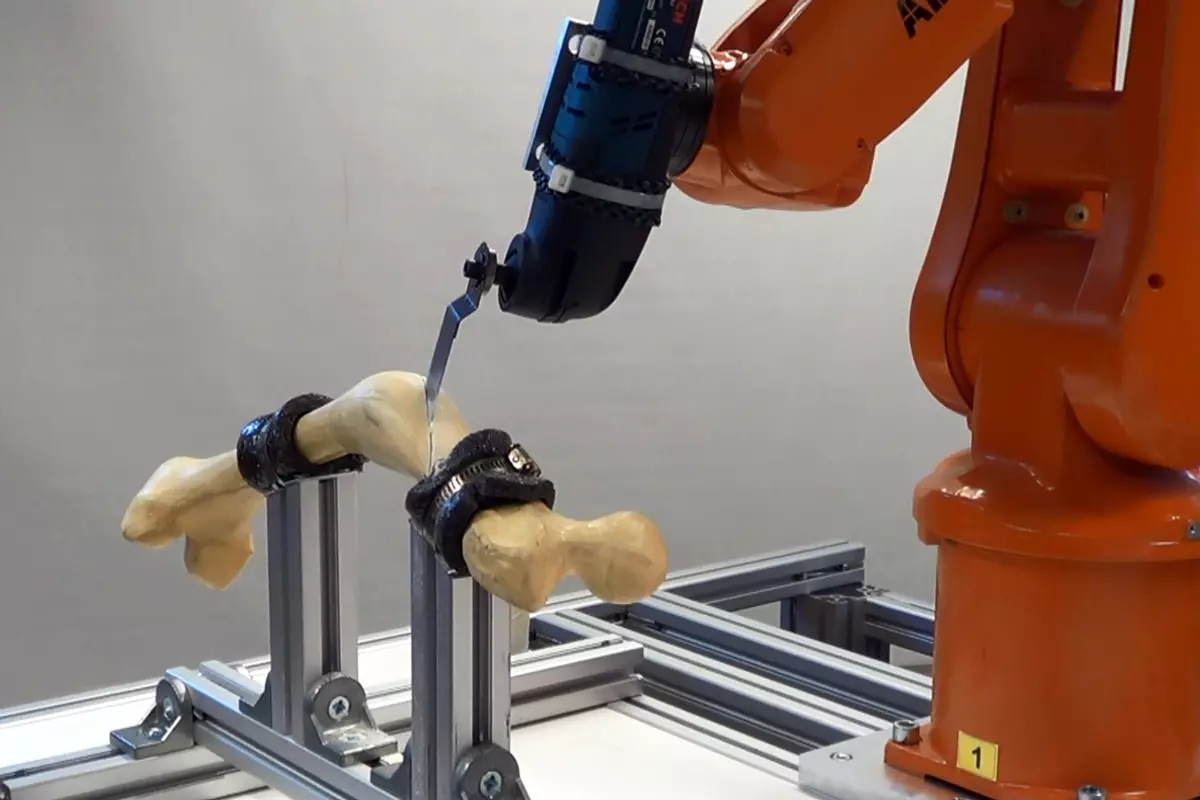
The goal of this Project thesis was to develop a tool to assist surgeons performing single-cut-osteotomies (surgical intervention). A software-planning-tool was developed and a possible implementation was tested using an industrial robot.
Even when treated carefully, fractures of long bones can grow together at an angle, which can have severe long-term consequences for patients.
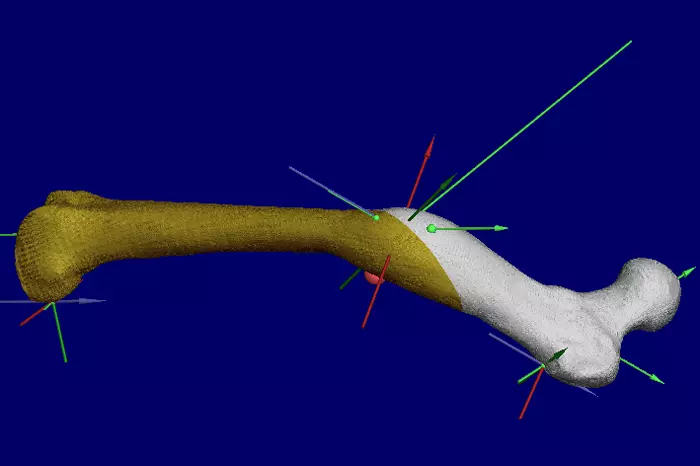
In many cases it is possible to bring back wrongly set bones into their original shape (length, angle, orientation) using a so-called single-cut-Osteotomy. This means that the bone is cut once (Single-Cut) and the two pieces are then rotated against each other along the cutting plane.
Since this procedure (especially the calculation) is comparatively complex, during an IMS Project thesis a software-tool was developed to helpsurgeons plan the procedure. The tool calculates cutting data, which then are transferred to an ABB IRB 120 robot.This was tested successfully in reality using a model of a thigh bone.
Videos
More Information
You can find further information about this project in the STZ-Artikel (PDF 219,5 KB)(in German).
Remote Control Application for the Mobile Robot FORBOT
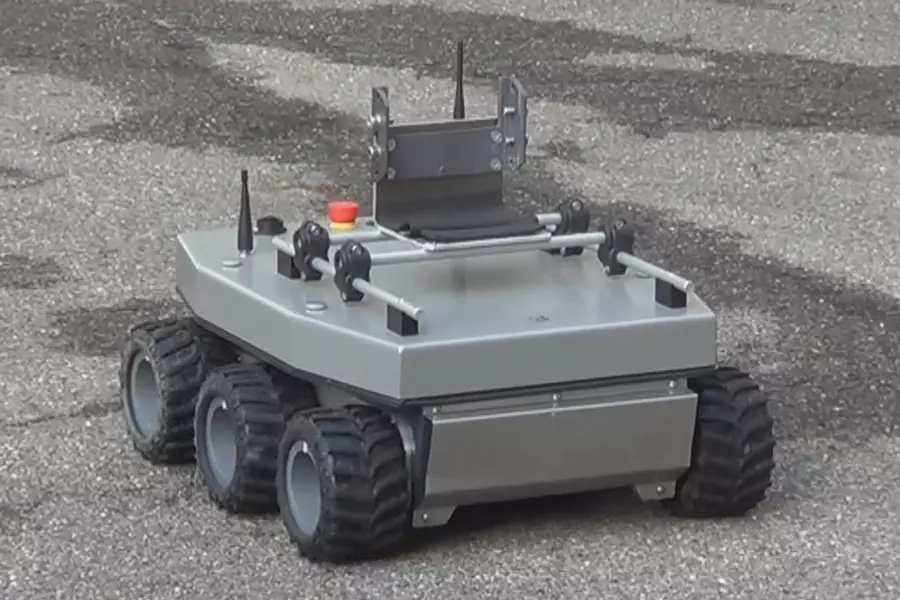

Today mobile robots move more and more independently even through areas with all kinds of obstacles. Since they are equipped with a complex system of sensors, they do not need to be constantly supervised by the operator. Real-time computers make sure that the signals from the sensors and the resulting control commands reach the motor controls in time and with the right priority.
The goal of this Project Thesis was to implementati a real-time-operation systems using a tablet control application for the mobile IMS robot FORBOT. After the evaluation of different systems a control computer with a real-time kernel was programmed and a control application developed in C++. This application provides intuitive wireless control of the robot through a tablet Computer.
Video
Pre-study for an interactive Billiard Robot
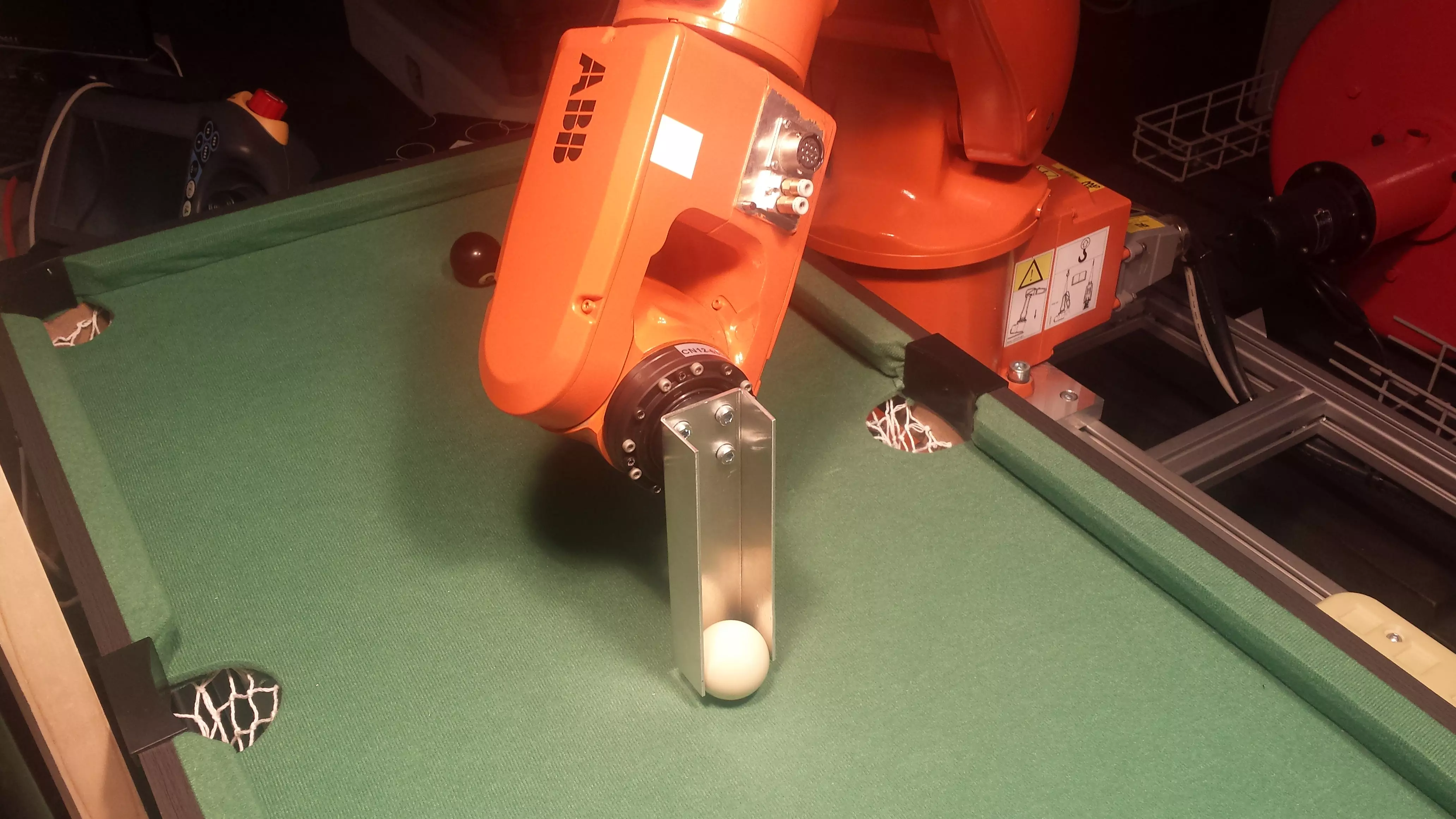
Goal of the Project Thesis was to evaluate whether it would be possible and worthwhile to develop a billiard robot similar to a chess computer.
In any good amusement arcade you can find at least one billiard table, which invites you to show off your billiards talent. But as it is in life there are good days and there are bad days. Sometimes there is not one successful hit, although one even is someone has a billiard table of their own at home. Unfortunately it is not too enjoyable to play against oneself. How much more fun it would be to own a billiard robot similar to a chess robot!
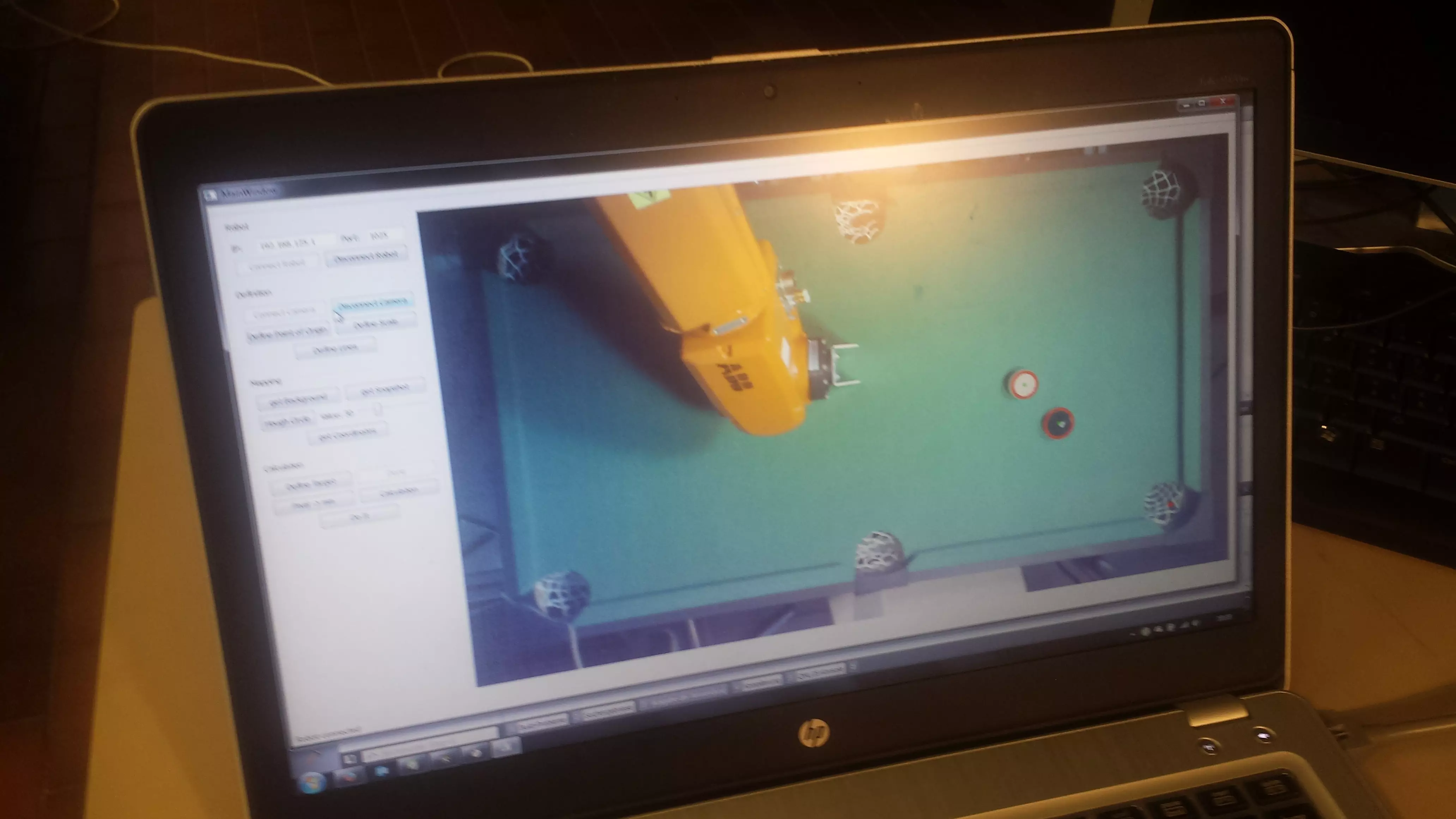
This project thesis deals with exactly this task. The goal of the Project Thesis was to evaluate whether it would be possible and sensible to develop a billiard robot. A complete game has not been played, but only the final hit with two balls. To be able to hit the ball in the right way, different problems have to be analysed and solved, such as the ball position on the table and the calculation of the hit.
To enable the robot to play billiards independently, it was connected to a control computer. This computer uses an industrial camera to take a picture of the ball and calculate its position on the table. When the positions of all balls are known, the target pocket can be identified and the calculation started. Using the result of the simulation, the computer transfers the calculated angle for the hit to the robot using TCP/IP. Together with the calculated position of the ball, the robot can pocket the ball.
At the moment precision remains a problem, since the coordinates of the image processing are not accurate yet. Nevertheless a good basis for further theses has been established, which may eventually lead to someone being able to play against a robot in an amusement arcade.